AI Agents at Work: Reshaping Enterprises with Smarter Automation
Learn and Discover What AI agents are and how AI agents are revolutionizing Human world by automating tasks, streamlining processes, and enhancing productivity.
It’s Monday morning, and the coffee hasn’t worked its magic yet. Meanwhile, your to-do list seems extremely large: maybe there are 10 emails and 50 slack messages waiting for you, you’re sorting through returns, reviewing new shipping invoices, updating field technicians, or streamlining IT support for employees.
Now, imagine delegating these tasks with a simple request to an AI agent — freeing you up to sip that second cup of coffee and focus on big-picture goals.
AI agents can work alongside you, managing tasks like scheduling meetings, sending reminders, or organizing your inbox. These are some of the easy and low risk tasks which agents can do for you. However , there are more complex tasks which agents can do which need a lot of smart decision making and usage of tools and customization.
In short, agents simplify daily chores, helping you work smarter, save time, and focus on what really matters.
The impact of AI agents
Source: Microsoft
Outline of the Blog
Introduction to Agentic AI: AI agents are intelligent systems with autonomy, memory, reactivity, proactivity, and collaboration capabilities. They are transforming industries like logistics, IT, and project management by automating and optimizing tasks.
Impact and Opportunities: AI agents streamline workflows, manage tasks like inventory and expense reporting, and enhance collaboration. They represent a shift in productivity, unlocking efficiency and improving decision-making.
The Road Ahead: AI agents are evolving with advanced reasoning, memory, and dynamic ecosystems. Their future potential includes transforming industries, enabling personal assistants, and redefining how work gets done.
Quotes by Industry leaders on the impact of AI and Agents
“Think of agents as the new apps for an AI-powered world,” says Jared Spataro, Microsoft’s chief marketing officer for AI at Work. “We’re rapidly adding new capabilities to tackle individuals’ biggest pain points at work and drive real business results.”
“AI agents will become our digital assistants, helping us navigate the complexities of the modern world. They will make our lives easier and more efficient.” – Jeff Bezos, Founder and CEO of Amazon
“AI agents will transform the way we interact with technology, making it more natural and intuitive. They will enable us to have more meaningful and productive interactions with computers.” – Fei-Fei Li, Professor of Computer Science at Stanford University
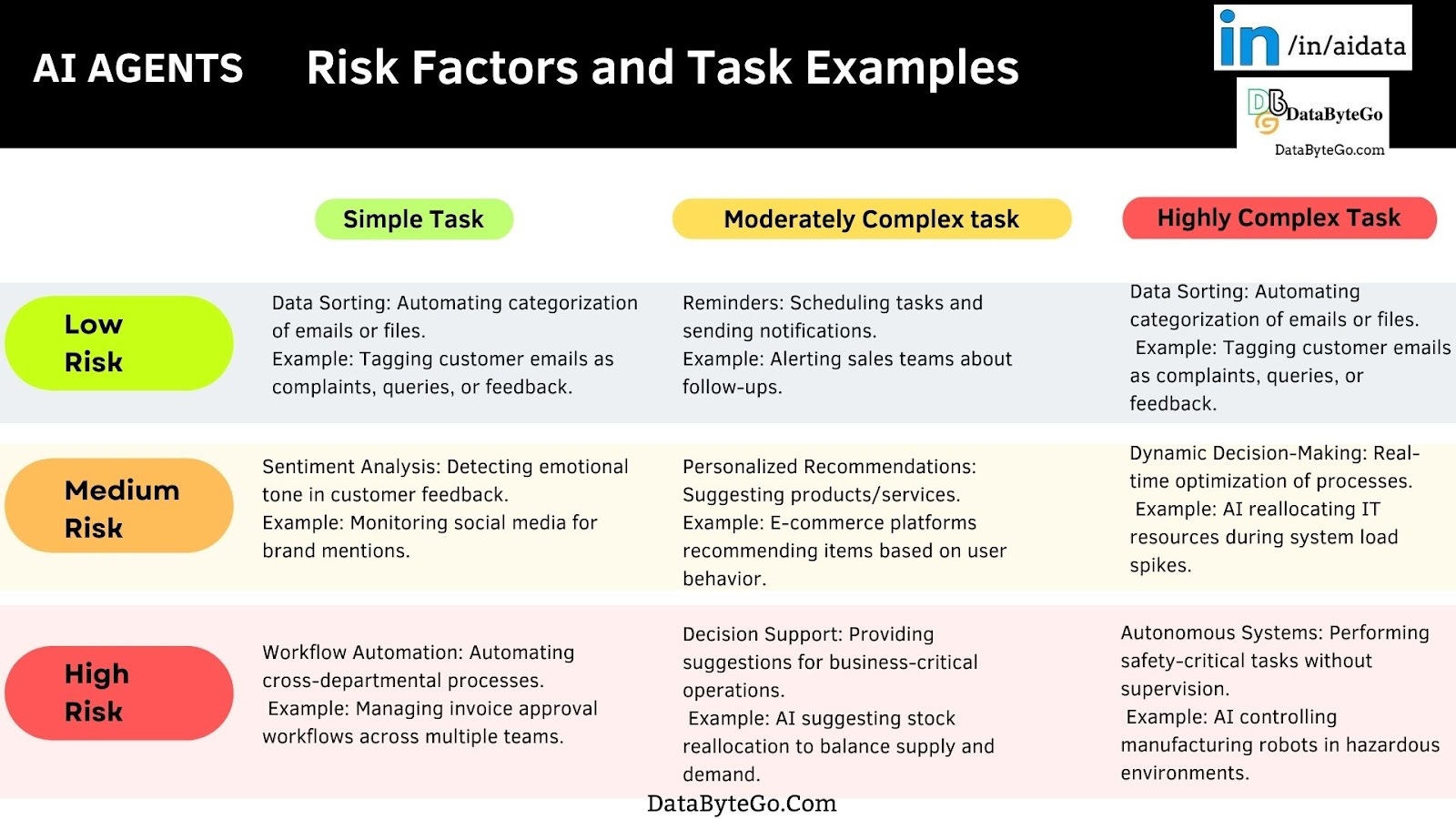
Complexity of tasks AI agents can perform and the risk associated with them
Source: Author
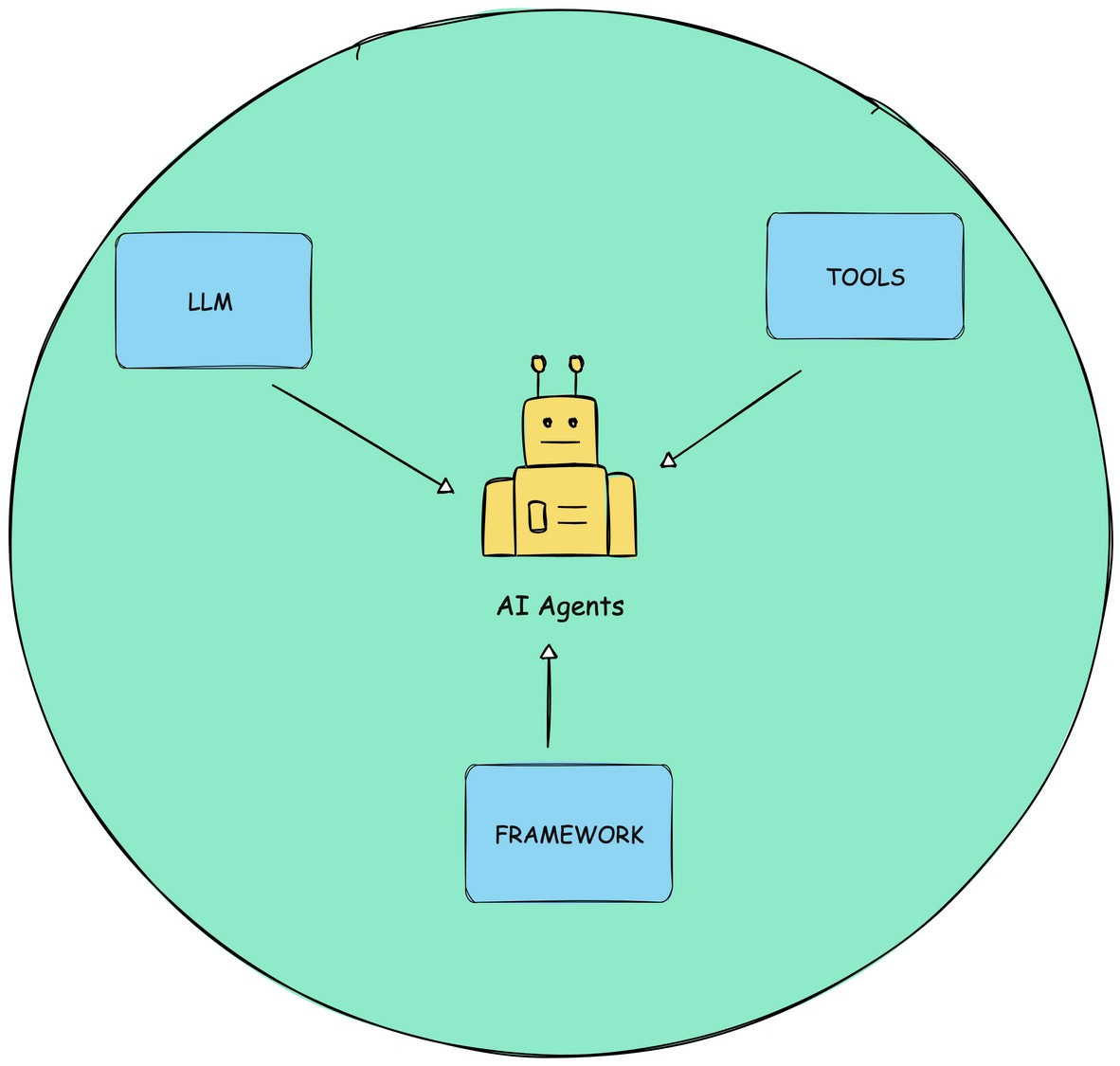
What are agents, anyway?
Source: Author
An agent powered by generative AI goes beyond just assisting you—it can work alongside you or even act on your behalf. Agents handle tasks ranging from answering questions to managing complex, multi-step processes. Unlike a typical personal assistant, agents can be customized with specific expertise.
For instance, you could create an agent that knows your company’s product catalog inside out. It could draft detailed responses to customer inquiries or automatically gather product details for an upcoming presentation. Some agents can even take direct action, like processing sales orders, freeing you to build stronger customer relationships. By handling routine tasks, agents can boost productivity across industries like manufacturing, research, finance, and retail—saving both time and money.
Picture yourself as a salesperson with ambitious quarterly targets. A Copilot or agents acts as your personal assistant, drafting emails, summarizing missed meetings, and designing polished sales presentations. Meanwhile, a specialized sales agent works in the background, finding new leads for you to pursue later. While Copilot helps with daily tasks, your customized agent leverages its unique skills to drive you toward meeting your quarterly goals.
Source: Microsoft
Agents are like layers on top of the language models that observe and collect information, provide input to the model and together generate an action plan and communicate that to the user — or even act on their own, if permitted. So both agents and models are equally important pieces of the puzzle, as far as generative AI tools go.
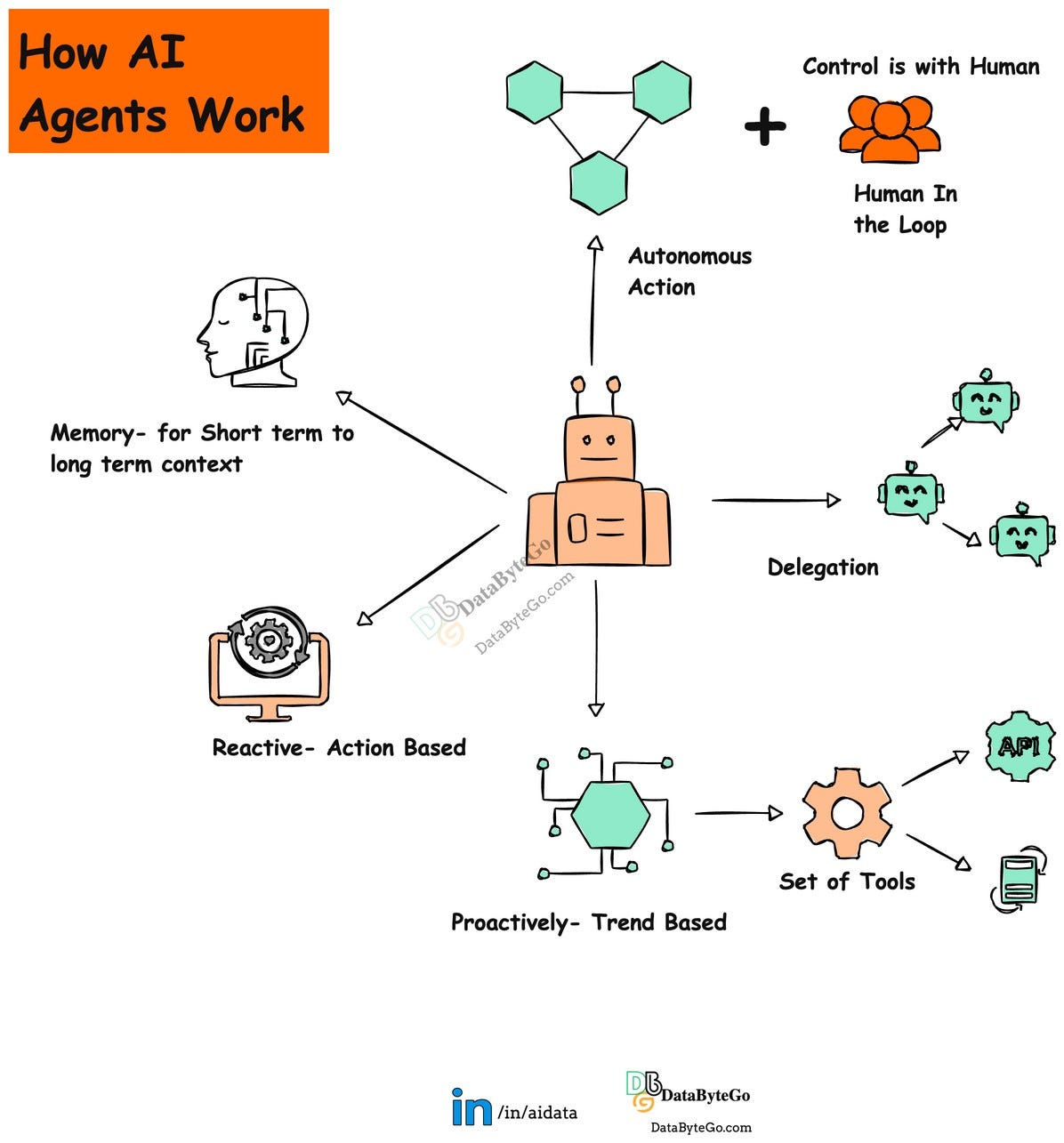
Other than LLMs intrinsic abilities, there are 5 other important characteristics of Agent:
Source: Author
Autonomous Actions
Agents can perform tasks independently by making decisions and taking actions without constant human input. However, keeping a human in the loop ensures better control and helps guide agents toward their goals.
Memory
Agents with memory can adapt to individual preferences by learning and evolving over time. This personalization builds stronger, long-term relationships between agents and users, allowing for more meaningful and tailored interactions.
Reactivity
Agents can understand and respond to changes in their environment by processing available information. This enables them to make decisions, provide relevant outputs, and offer context-aware assistance based on real-time data.
Proactivity
Agents can take initiative by planning, prioritizing, and completing tasks using various tools like web searches, code interpreters, or data scraping. Currently, this is mainly achieved through API calls and function executions.
Social Ability
Agents can collaborate with humans or other agents by delegating tasks, maintaining defined roles, and working toward shared goals. This capability ensures effective communication and smooth teamwork.
To be autonomous you have to carry context through a bunch of actions, but the models are very disconnected and don’t have continuity the way we do, so every prompt is in a vacuum and it might pull the wrong memory out. The work with entitlements and tools is making sure agents have secure access to, or are entitled to, information they need in order to accomplish things for you, with your permission — like who your boss is, for example — and to the computer programs they need to take action on your behalf, like Teams and PowerPoint.
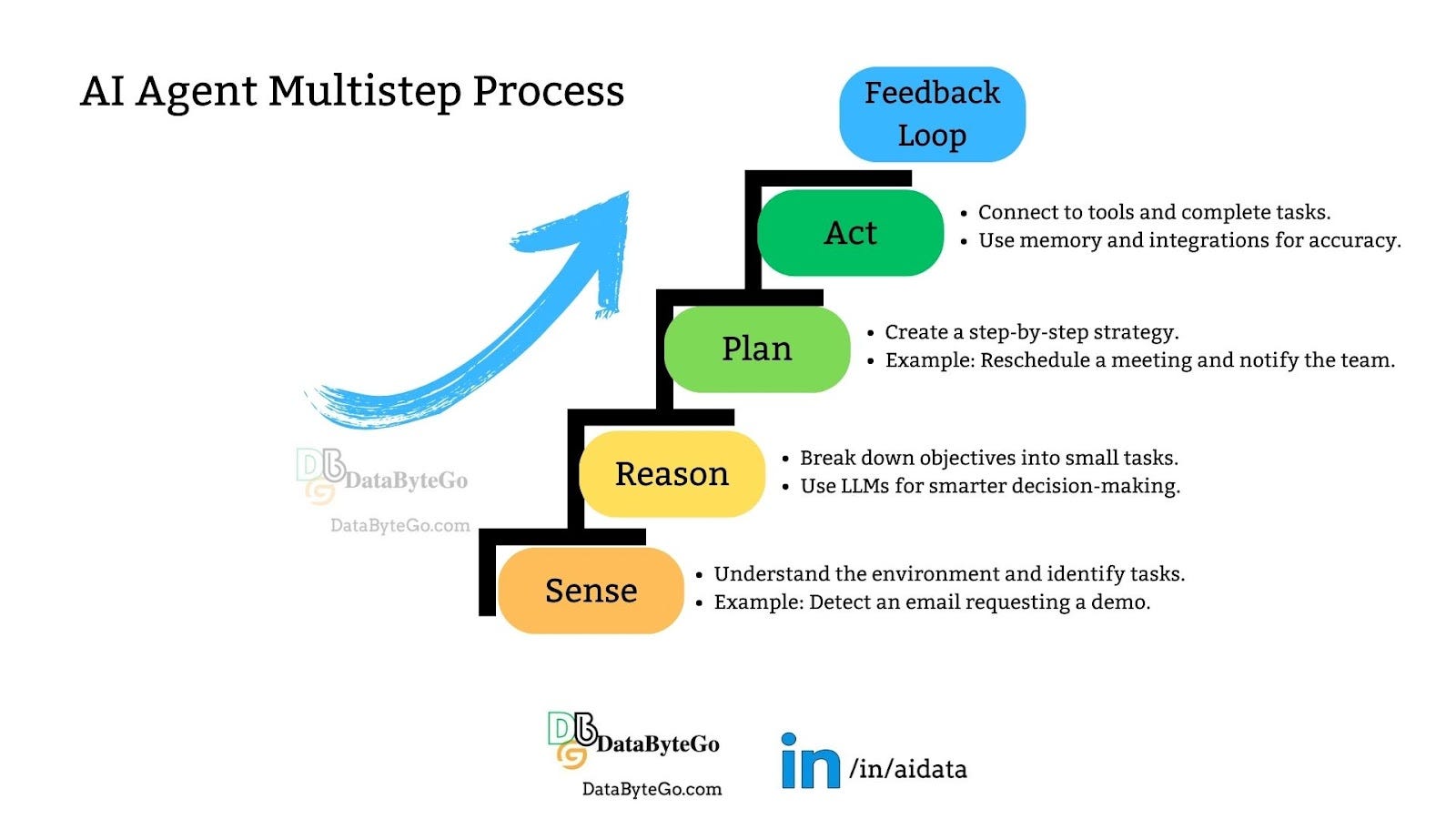
How AI agents work
Agents go through a multi-step process as shown in Figure 1.
Sense
Agents perceive and interpret their environment to identify tasks and determine desired outcomes. For example, an agent integrated with an email client like Microsoft Outlook could detect a prospect's request for a demo. Acting as a digital Sales Development Representative (SDR), the agent processes the email and responds accordingly, automating tasks such as scheduling meetings or sending relevant information.Reason
Once the agent understands its objective, it breaks it down into specific tasks using advanced reasoning powered by a Large Language Model (LLM). Techniques like chain-of-thought reasoning, ReAct (Reason + Act), and few-shot learning help the agent convert complex goals into actionable steps. This structured thinking enables efficient task management and decision-making.Plan
Agents create a detailed action plan based on the tasks identified. For example, an SDR agent tasked with rescheduling a meeting might:Update the meeting time in the calendar.
Send a confirmation email to the prospect.
Notify the internal team about the changes.
By planning each step methodically, the agent ensures tasks are completed efficiently while staying aligned with business goals.
Act
Agents execute tasks by connecting to appropriate systems securely and ensuring compliance with governance standards. They can use Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) for accurate information retrieval and integrate with external applications for long-term memory. For instance, an agent might access a customer’s purchase history stored in a CRM system to personalize its response. This enables smooth, context-aware task completion.
Agents mirror real-life workflows across industries, from booking flights to processing bank transactions. They integrate seamlessly with enterprise systems, handling tasks autonomously while escalating complex issues to humans when needed. Looking ahead, personal AI assistants could become part of daily life—helping students with homework, managing travel plans, or even revolutionizing ERP systems by disrupting traditional models.
Adoption Trends
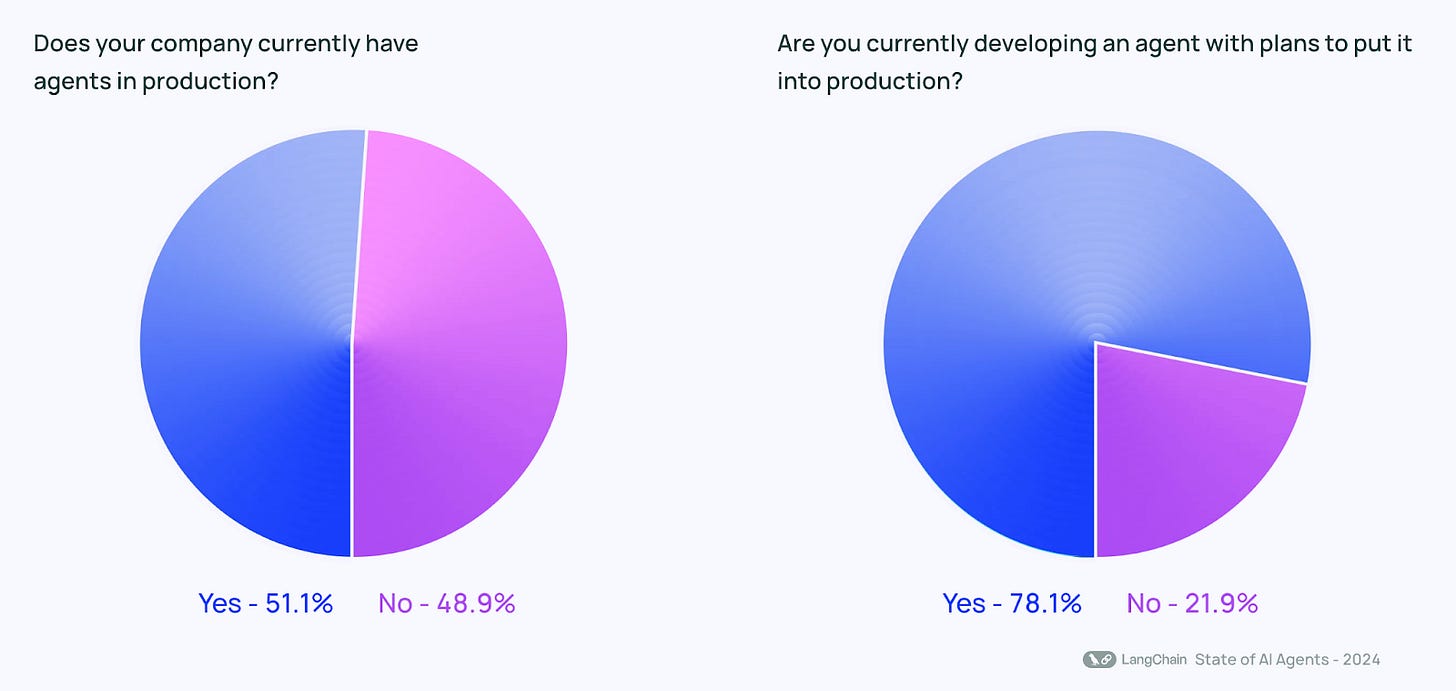
AI agents are gaining momentum despite some skepticism. According to LangChain’s State of AI Agents survey(LangChain’s State of AI Agents survey of 1,300 respondents), over 50% of companies already have agents in production, and nearly 80% are actively developing them.
Future- the biggest impact of AI agents
AI agents are rapidly gaining traction. LangChain’s State of AI Agents survey of 1,300 respondents revealed that over 50% of companies already have agents in production, while nearly 80% are developing them.
AI agents are set to redefine how people work by simplifying complex tasks and enhancing productivity. Creating and deploying AI agents is becoming as straightforward as using everyday business tools, making the technology accessible even to those without coding experience.
With intuitive platforms, anyone can build agents by connecting them to relevant business data such as emails, reports, and customer management systems. These agents can then perform tasks, provide insights, and automate workflows based on real-time data.
Advanced AI models with strong reasoning capabilities allow agents to tackle complex, multi-step tasks. For example, an IT support agent could gather information about a technical issue, consider previous troubleshooting steps, and generate a personalized action plan for resolution.
As AI agents continue to evolve, they will become indispensable tools across industries, transforming how businesses operate and helping individuals focus on more strategic and creative work.
Assessing risk for autonomous action
Agents capable of autonomous action introduce additional safety considerations. Since they can make decisions and take actions independently, ensuring they operate within defined boundaries becomes crucial. This requires minimizing errors and carefully managing potential risks.
Responsible AI principles play a central role in assessing and mitigating these risks. Organizations must adopt strict data governance, access management, and security protocols. Monitoring tools can track how agents are used, measuring both adoption and business impact.
To maintain accountability, many systems implement “human in the loop” processes. For example, an agent might draft a customer email, but a person would review and send it. Additionally, developers can audit agent actions to understand what decisions were made and why.
The key to success lies in thorough testing, continuous monitoring, and moderation. Organizations should start with well-defined, lower-risk use cases, gradually scaling up as they gain confidence in the system’s reliability and effectiveness.
Looking back — and into the future
Technologists have long been excited by the idea of autonomous systems working side-by-side with people to help them, says Kamar, who has been working on AI agents since 2005 and even wrote her Ph.D. thesis on the topic in 2010. The hurdle was that “we lacked that general problem-solving power” on the back end, she says.
With LLMs, “we finally have this missing component,” she says. “Now we can bring back a lot of the ideas from our decades of research.”
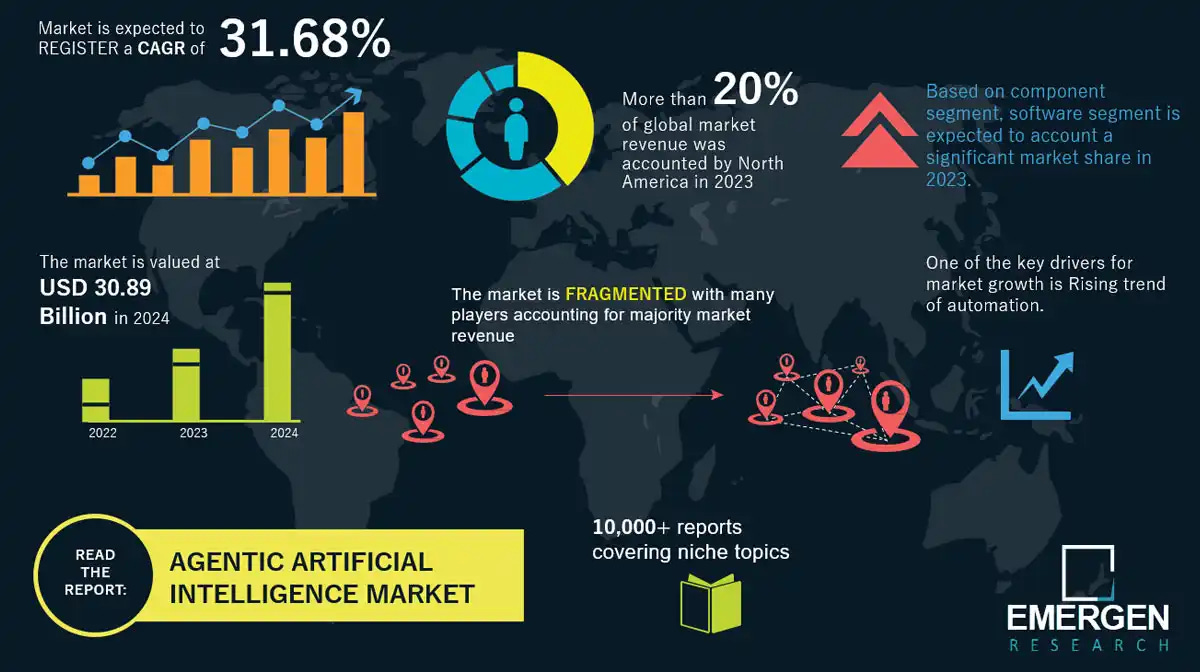
Source: Emergenresearch
The idea of autonomous systems assisting humans has long fascinated technologists. For years, the challenge lay in the lack of general problem-solving power needed for such systems to function effectively. With advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs), that missing piece has finally emerged, enabling decades of research concepts to become practical realities.
Looking ahead, the future of AI agents points toward the development of a dynamic ecosystem—similar to how app marketplaces revolutionized smartphone usage. AI agents now possess essential building blocks like observing, reasoning, and acting. For instance, they can detect when a meeting is running late and automatically adjust subsequent appointments, showcasing proactive task management capabilities.
As these agents continue to evolve, they are becoming more autonomous, driven by innovations in memory, contextual understanding, and dynamic task execution. They’re reducing workplace friction by streamlining processes like expense management, project coordination, and task scheduling. In industries such as logistics, agents can manage inventory by detecting shortages and placing restock orders, ensuring smooth business operations and improved customer satisfaction.
AI agents aren’t just tools; they represent a shift in how work gets done. They unlock new opportunities for collaboration, enabling businesses and individuals to operate more efficiently. As they become more capable, AI agents are poised to redefine productivity and reshape the future of work. This isn’t just technological progress—it’s the beginning of a new era in human-AI collaboration.
Reference read
https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/worklab/ai-is-already-changing-work-microsoft-included
https://www.weforum.org/stories/2024/12/closing-ai-equity-gap-trust-and-safety/
https://www.emergenresearch.com/industry-report/agentic-artificial-intelligence-market
"AI Agents That Matter" https://arxiv.org/abs/2407.01502
"Agent AI: Surveying the Horizons of Multimodal Interaction" https://arxiv.org/abs/2401.03568
"An Interactive Agent Foundation Model" https://arxiv.org/abs/2404.01234
"Agentic Intelligence: Applications and Opportunities"
https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/ai"OpenAI’s Vision on AI Agents in Practice" https://openai.com/blog
"Google’s Research on Autonomous AI Agents"
"AI Agents Transforming Business and Collaboration" https://aws.amazon.com/blogs
"LangChain State of AI Agents Survey" https://www.langchain.com/stateofaiagents
"Agentic AI in Emerging Markets"